- Home
- About Doctor
- For Patients
- Gall Stones
- Appendicitis Treatments
- Obesity
- Oesophagus Cancer
- Gastric Ulcers And Treatments
- Duodenal Ulcers
- Stomach Cancer
- Liver Diseases
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Pancreatitis diseases and tumours of the pancreas
- Perforation of the intestine
- Abdominal Trauma
- Jaundice Treatment
- Crohn’s Disease
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Colon Polyps
- Piles
- Hernia
- Fistula
- Cancers
- Thyroid Disorders
- Swelling and Abscesses anywhere in The Body
- Surgeries Offered
- Gastrointestinal Surgeries
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy
- Surgery for GERD
- Trauma Surgery
- Surgeries for Obstructive Jaundice
- Surgeries for the Pancreas
- Surgeries on the Stomach
- Bariatric Surgery
- Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastronomy
- Hernia Surgery
- Breast Surgery
- Small and Large Intestine Surgeries
- Colorectal Surgery
- Testimonials
- Blogs
- FAQs
- News And Events
- Gallery
- Contact Us
- Book an Appointment
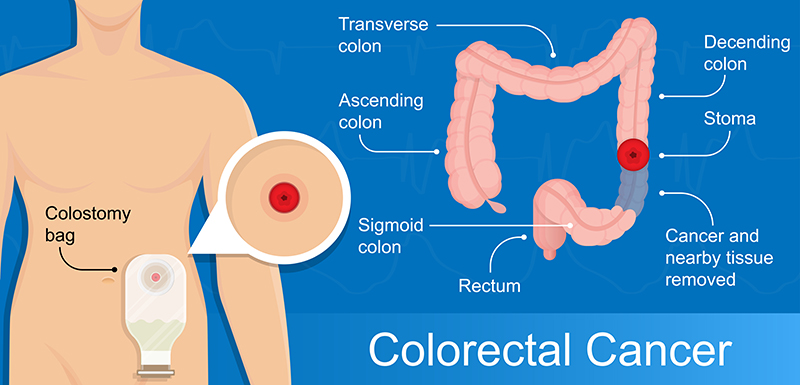
Rectal Cancer
Rectal cancer is the development of malignant tissues in the rectum. It is the third most common type of cancer in both men and women in the us. There is a necessity to go through various scans to understand the development of cancer. The breakthrough technologies enable us to provide you the best rectal cancer treatment in Chennai. Dr. Deepak is very popular as known as the best colorectal surgeon in Chennai. With the expertise of most competent cancer specialist in chennai, an effective treatment plan could be devised to tackle this disease.
Cancer cells emanate in the tissues of the rectum causing rectal cancer. Colorectal cancer can occur either in the rectum or in the colon. Colon and rectal cancer extensively comprise of adenocarcinomas (about 98%). Rectal cancers are also inclusive of carcinoid, sarcoma and lymphoma. Both colon and rectal cancers may undergo similar screening recommendations. Squamous cell carcinomas are anal carcinomas that develop in the area commencing from the rectum to the anal verge. Every 6 days the mucosa in the large intestine regenerates during which time the crypt cells migrate to the surface. Their ability to replicate is lost when they encounter differentiation and maturation.
Causes and risk factors
The development of colorectal cancer is sporadic and the exact etiological factors are unknown.
- Family and medical history: Women with a history of breast, uterus or ovarian cancers are at a high risk of developing the disease. If an individual’s first-degree relatives such as siblings, parents and children have had colorectal cancer, then the person is more likely to develop it themselves.
- Genetic disorders: Genetic components play a significant role in the development of colorectal cancer. 2% of all colorectal cancers occur due to the alteration of the HNPCC gene. FAP or familial adenomatous polyposis is caused due to alterations in the APC gene.
- IBD or inflammatory bowel disease: Crohn’s disease causes inflammation of the colon increasing the risk of the development of colorectal cancer.
- Lifestyle and environmental factors: High ingestion of alcohol, smoking and consumption of high-fat foods increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Cholecystectomy: The cholecystectomy procedure allows the free flow of carcinogenic bile acids and their byproducts enhancing intestinal degradation due to bacteria.
Signs and Symptoms
- Prolonged rectal bleeding – this could also be due to the presence of hemorrhoids
- Blood mixed with the stool
- Anal bleeding
- Bowel obstruction
- Presence of a large rectal mass disallowing the normal passage of stools resulting in severe constipation and pain
- Narrow size of stool – pencil-thin stools are a result of obstruction due to rectal cancer
- Sensation of incomplete evacuation of stools
- Unexplained weight loss
Diagnosis
- Physical examination will check for metastatic lesions, enlarged lymph nodes, the size and location of cancer.
- DRE or digital rectal examination is done to detect the presence of abnormal lesions. The size, ulceration and existence of pararectal lymph nodes of rectal tumours are assessed.
- Laboratory tests will include CBC, serum chemistry, carcinoembryonic antigen test and cancer antigen 19-9 assay. Screening techniques conducted are:
- FOBT – Guaiac-based fecal occult blood test
- SDNA – Stool DNA screening using polymerase chain reaction
- FIT – Fecal immunochemical test using monoclonal antibody assay
- Rigid proctosigmoidoscopy to estimate the size of the lesion and degree of obstruction
- FSIG – Flexible sigmoidoscopy
- DCBE – Double-contrast barium enema
- CTC – CT Colonography or virtual colonoscopy
- FFC – Fiberoptic flexible colonoscopy
Treatment and Medication
Surgery and radiotherapy are options to be considered for the treatment of rectal cancer. Medication with antineoplastic agents helps to induce remission and downstage cancer thus preventing complications.
We conduct laparoscopic surgery for the complete excision of rectal cancer. Met the chief gastro specialist in Chennai and get resolved from the rectal cancer.
Ask doctor
Testimonials
 Very practical approach to my dads gallbladder stone problem .. Surgery was explained well by diagrams and he performed the surgery by key holes which made it pain free for my dad . I had consulted many in the last 1 month including
Very practical approach to my dads gallbladder stone problem .. Surgery was explained well by diagrams and he performed the surgery by key holes which made it pain free for my dad . I had consulted many in the last 1 month including 
Subramanian
Read More The doctor was helpful. He worked with me to select the best option for treatment and helped finalize treatment. He ensured that my appointment went ahead as planned and followed up rigorously post op too. Scar was a bit larger
The doctor was helpful. He worked with me to select the best option for treatment and helped finalize treatment. He ensured that my appointment went ahead as planned and followed up rigorously post op too. Scar was a bit larger 
Mehul Kain
Read More The doctor was helpful. He worked with me to select the best option for treatment and helped finalize treatment. He ensured that my appointment went ahead as planned and followed up rigorously post op too. Scar was a bit larger
The doctor was helpful. He worked with me to select the best option for treatment and helped finalize treatment. He ensured that my appointment went ahead as planned and followed up rigorously post op too. Scar was a bit larger